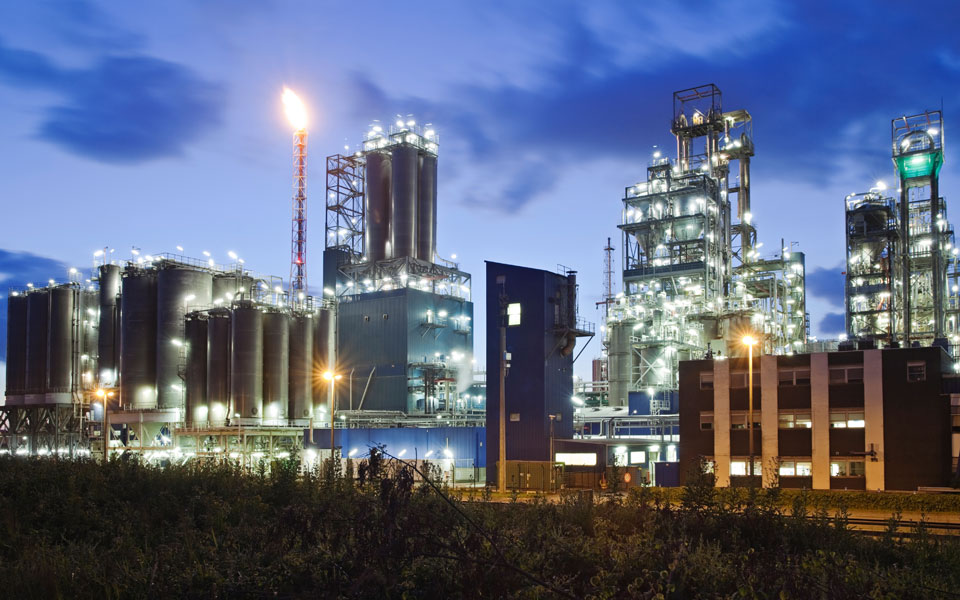
Chemical applications
Today, many applications in chemical systems engineering cannot be implemented without plastics and elastomers. Our extensive portfolio offers solutions for your corrosion problems under extreme environmental conditions. Fluoroplastics such as PFA, ECTFE, PCTFE, PTFE, PVDF or technical plastics such as PEEK, PPS, PP and PE as well as sealing materials such as FFKM, FKM, EPDM, NBR are available in numerous different dimensions. For conveyance of liquid and gaseous media, we also offer an extensive program of suction and pressure hoses. We would be pleased to support you in selecting materials and components in order to ensure that you get the best and most cost-effective solution.
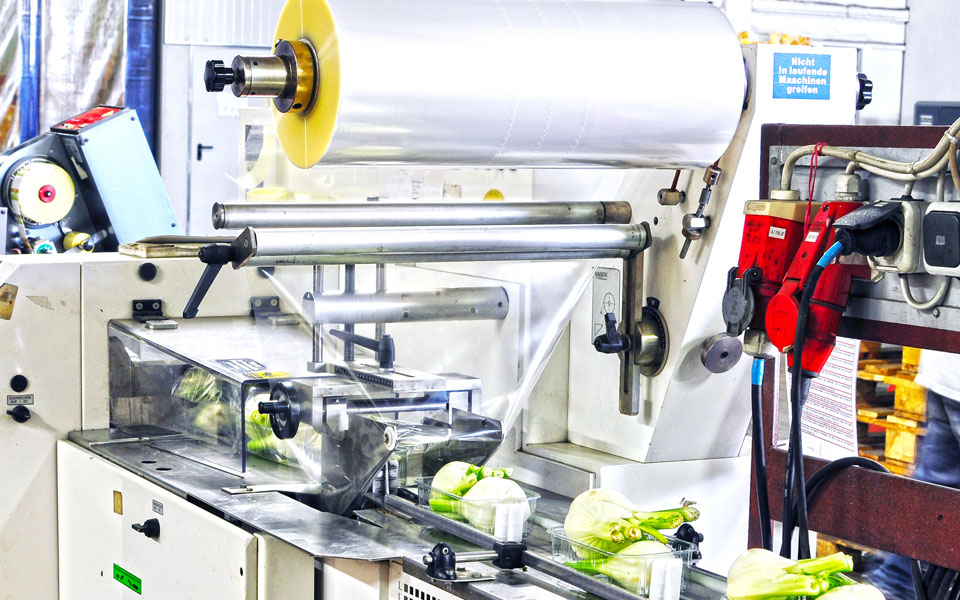

Foodstuff engineering
Technical high-performance plastics, elastomers as well as our foodstuff hoses make a significant contribution to increasing production efficiency and to product quality in the foodstuff industry. Consumers profit from these improved processes and are right to expect the use of the most demanding safety standards in producing food and beverages. The foodstuffs industry profits from our extensive portfolio ranging from PE up to PEEK materials as well as from our extensive industry know-how. Apart from the known standards, our portfolio also includes metal detectable and antistatic materials.

Sliding and wear applications
Specially developed technical plastics are increasingly used as substitute materials for brass, stainless steel, aluminum and ceramics in bearing and sliding applications. Typical areas of application are bearings, e.g. bushings, pressure plates, guides, components with high dimensional stability for precision mechanics (bushings, sliding rails, gear wheels, rollers, pump components, linings). Elastomers such as PU and natural rubber are used in applications that require good damping characteristics apart from low abrasion. Specially developed materials that are resistant to abrasion are used in our hoses for transporting abrasive materials.
Advantages → Longer service life → Elimination of lubrication requirement → Reduced wear on mating parts → Low density and hence lower inertia forces → Mechanical dampening [noise reduction] → Faster plant operation [higher line speeds] → Lower power requirement to run plants → Chemical and corrosion resistance and inertness.

High-temperature applications
High-temperature plastics and elastomers are used in many areas. The high temperatures may act from the external or occur in sliding friction applications due to friction heat. Schmidt + Bartl high-temperature materials cover temperatures for continuous use from 150°C to 310°C. Our high-temperature hoses are used in conveyance of hot, liquid or gaseous media.
Conductive
The material group of conductive plastics and elastomers comprises electrostatically dissipative plastics as well as electrically conductive materials. Electrostatically dissipative materials are predominantly used in applications with conveyance of electronic components as voltages of merely 100 V can lead to the irreversible destruction of circuits. Electrically conductive materials are predominantly used in systems that represent a fire hazard in which voltage peaks that are not dissipated can lead to sparking, which can cause fire or even explosions. We offer a large variety of electrically conducting hoses for transporting explosive media.
Medical & pharmaceutical engineering
Schmidt+Bartl offers an extensive portfolio of semi-finished plastic products, elastomers und hoses that meets the high demands of medical and pharmaceutical engineering and conform to FDA, ISO 10993 and USP standards. This saves testing costs and time and assures gapless traceability from the raw material to the semi-finished product. The modern portfolio of Schmidt+Bartl replaces existing material solutions based on a combination of features such as weight reduction, compatibility with common sterilization procedures, x-ray transparency and resistance to high-energy radiation.
Advantages → Testing for biocompatibility → Very good resistance to cleaning and disinfection agents → Resistance to common sterilization procedures → Lower density and hence lower inertia forces.